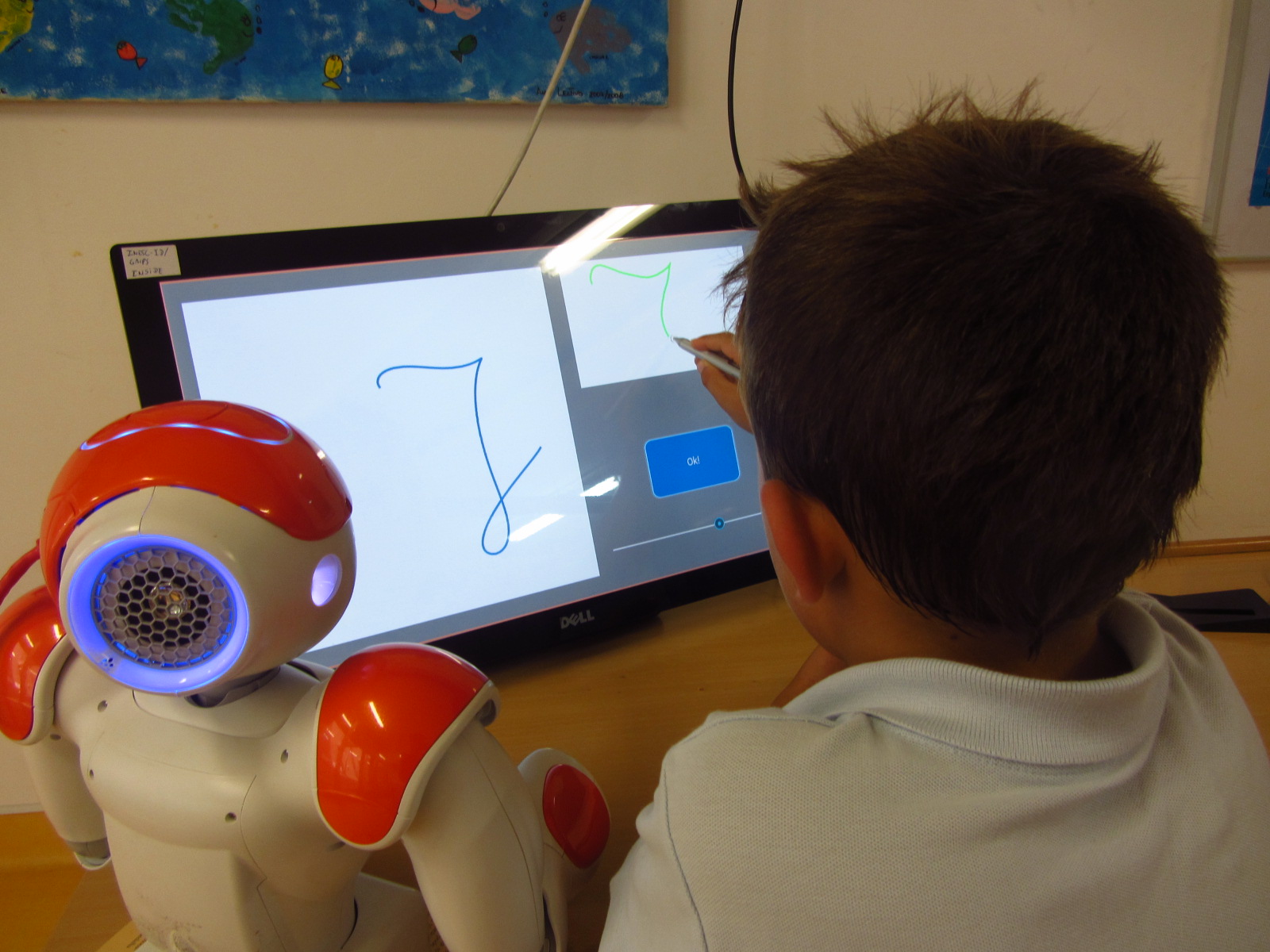
Human-robot interaction for children handwriting acquisition - CoWriter
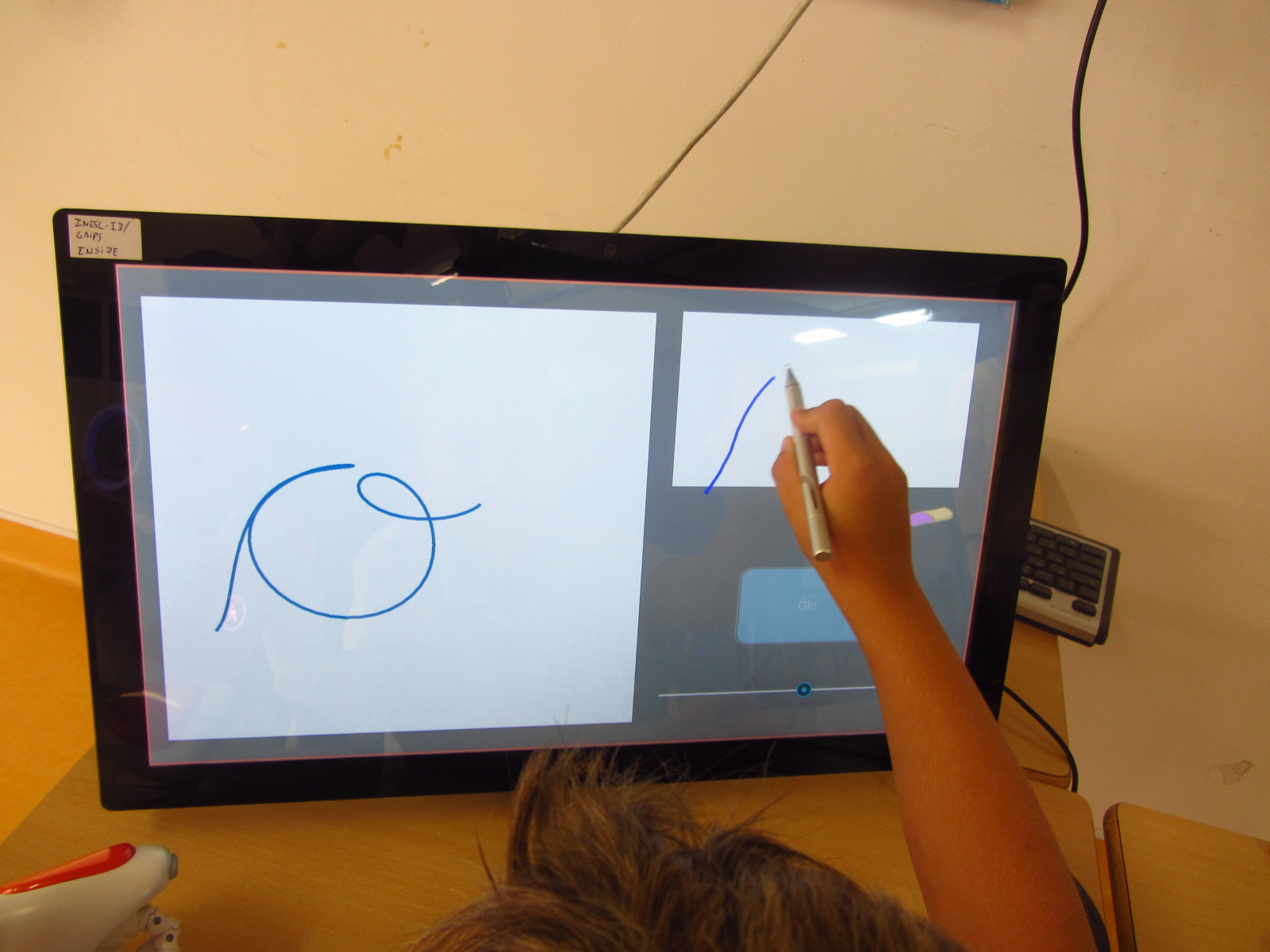
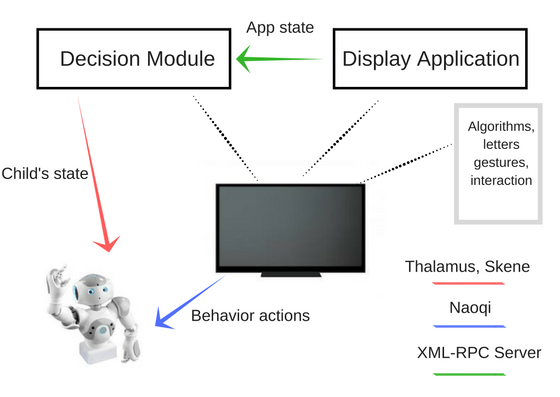
This research contributes to the CoWriter project, which aims to build a robotic system that interacts with children to help them to acquire handwriting skills. The research exploits the idea of learning-by-teaching framework: the robot plays the role of a learner while children polish their skills in teaching the robot.
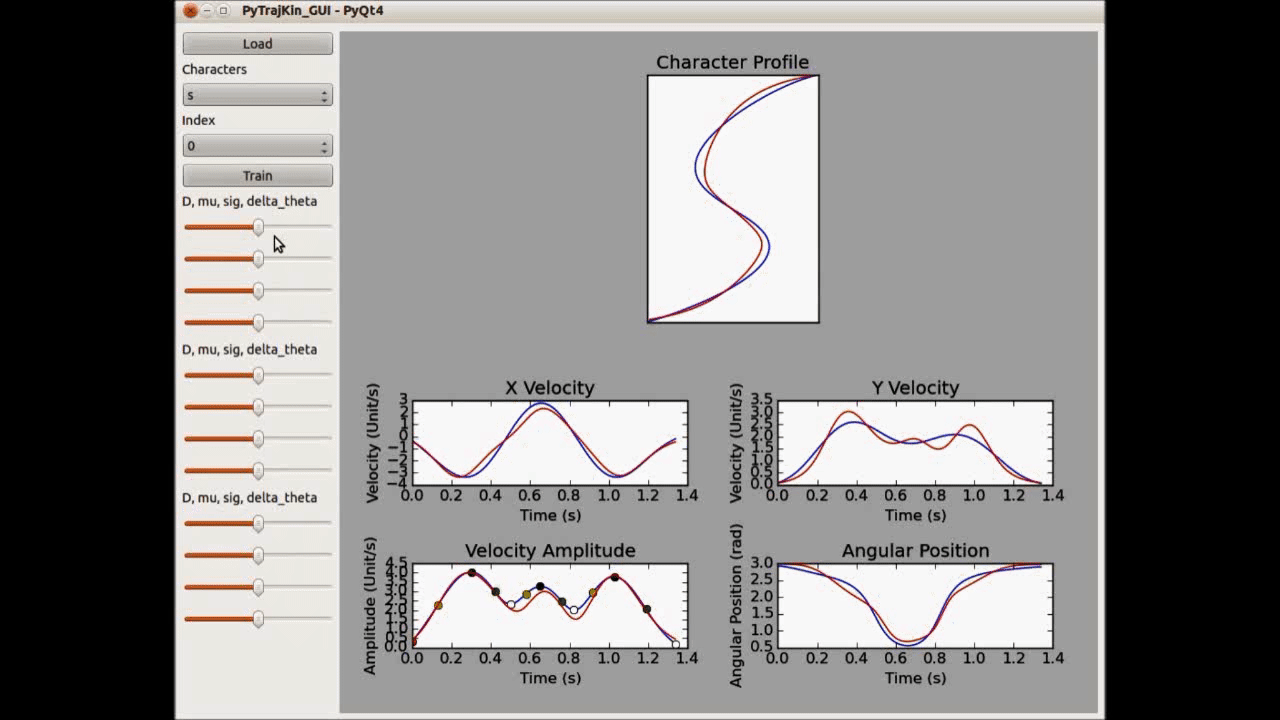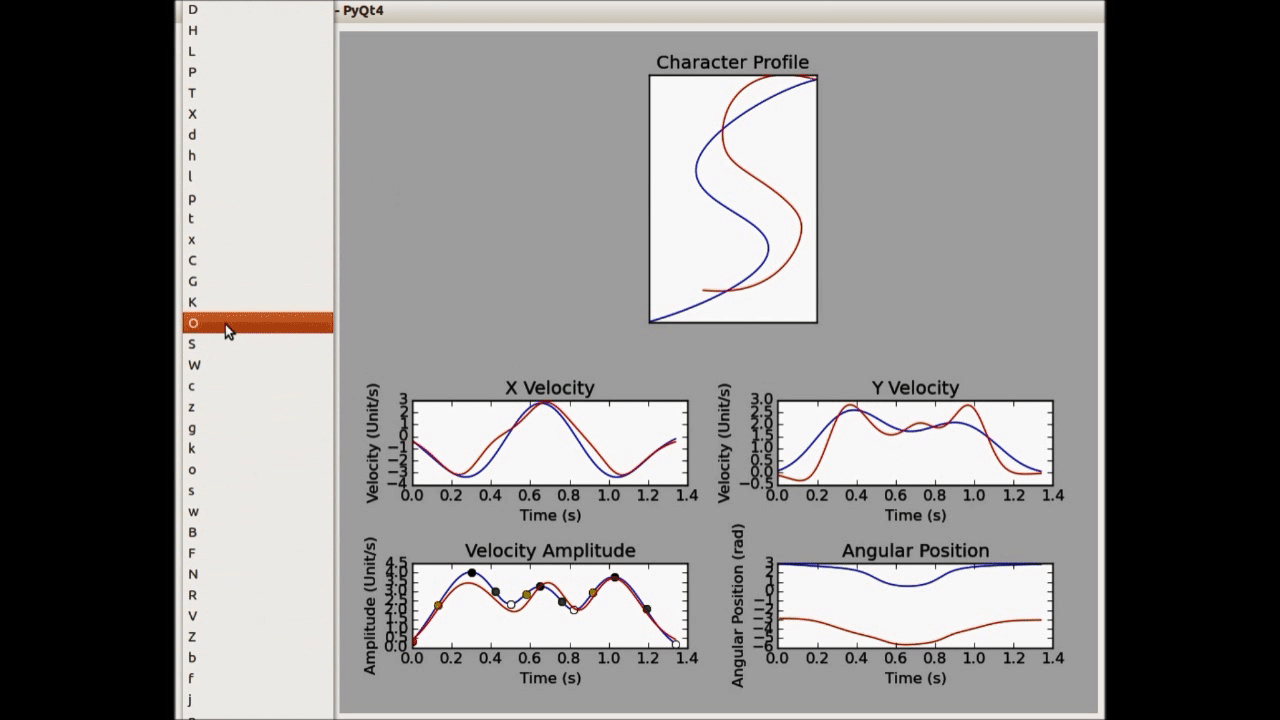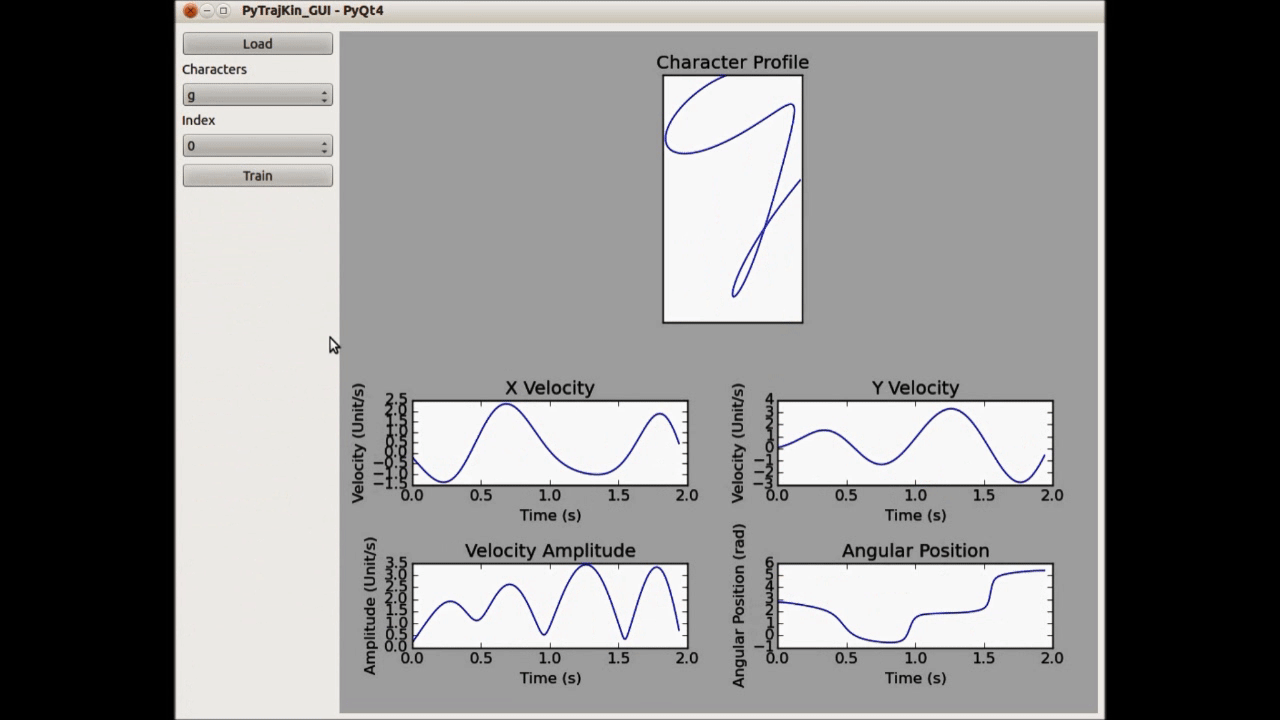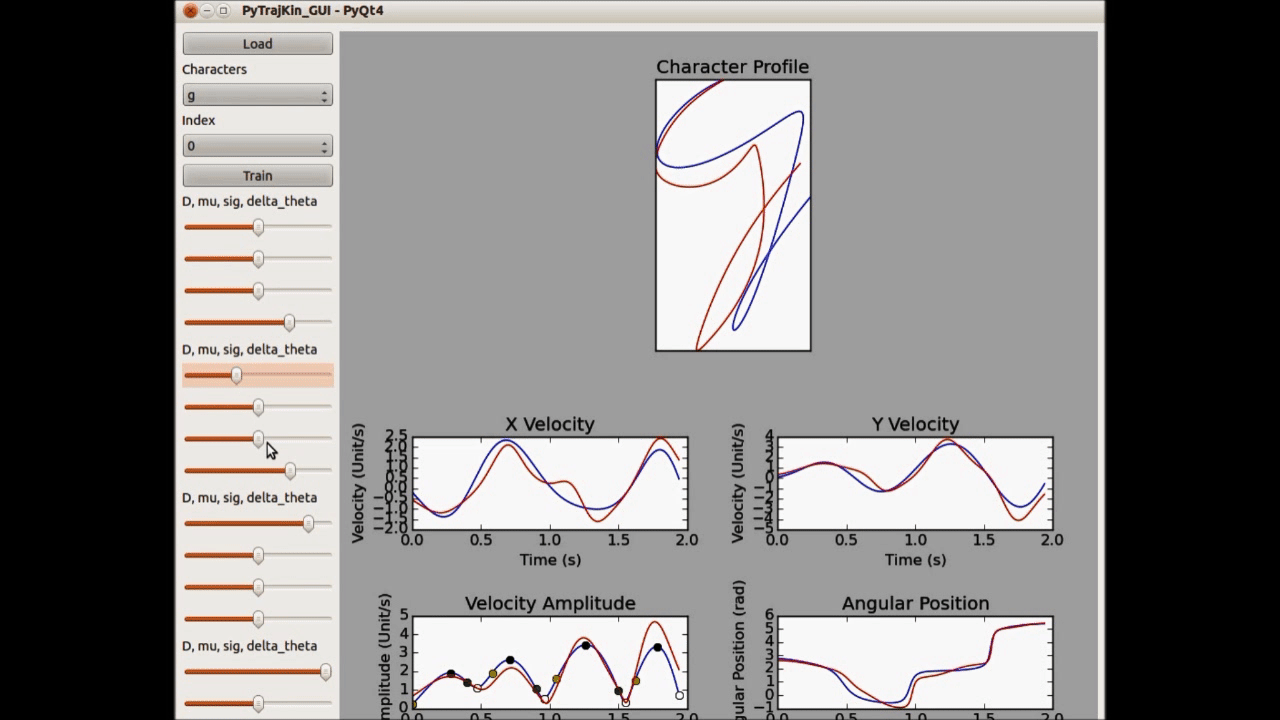
Machine learning techniques are used to learn from adult handwriting examples and generate similar/poorly-written samples by perturbing the model parameters. However, it is inadequate to learn with a direct feature representation, such as the coordinates of 2D points. Natural handwriting movement has many informative features in terms of motion smoothness, stroke segmentation and path geometries. A perturbation in such a feature space can be much more effective and intuitive to generate desired handwriting variations. Bearing this in mind, we learn the generative process with a kind of lognormal human kinematics model (see O’Reilly and Plamondon, Pattern Recognition, 2009). The parameters of lognormal model correlate to some useful kinematic and geometric features of handwriting motion, such as stroke velocity and angular positions. The learned model is a probabilistic distribution over these feature parameters, which manages to generate human-like dynamical handwriting motion if we take samples from the parameter configurations with a high probability mass.








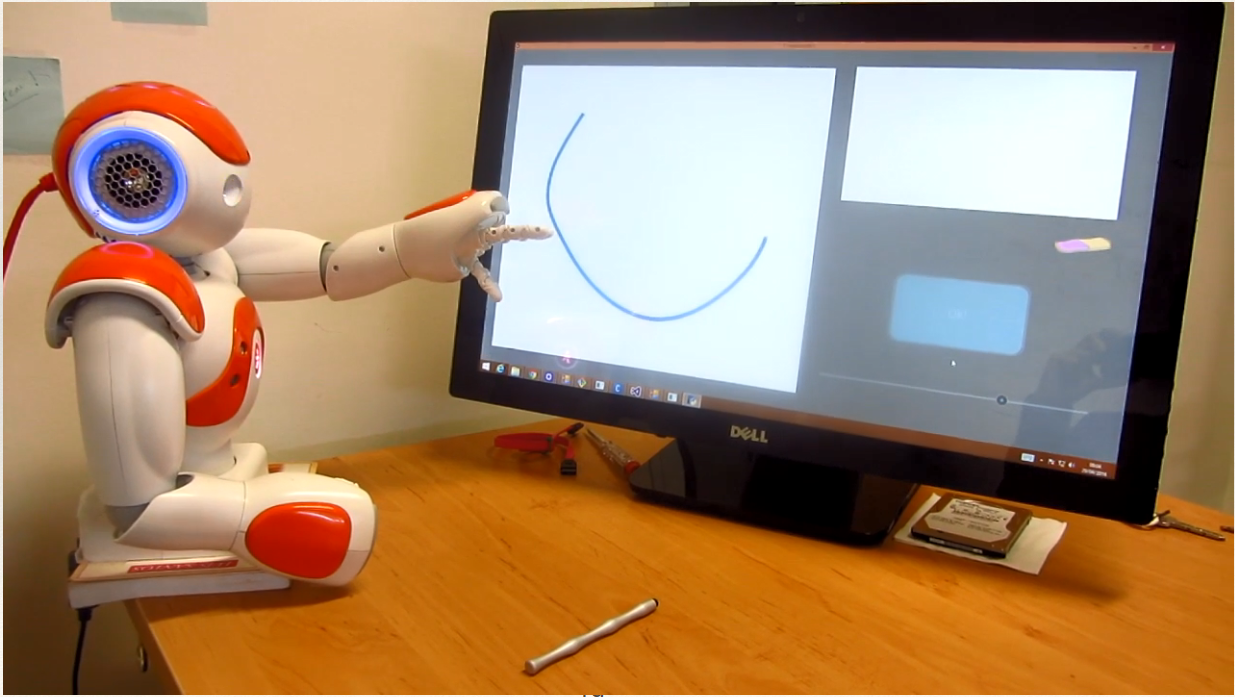
On the other hand, we can also generate unnatural letter profiles with unlikely parameter configurations. In fact, the deformations can be controlled as there is a clear connection between the stroke geometry and magnitude of feature parameters (see the left figure below). We use these models in an HRI system, where the robot demonstrates three typical children handwriting errors in the beginning and gradually improves during the learning session. Human studies show that children are aware of the learning capability of robots and can benefit from interacting with such a robotic companion.
Find more in:
Papers:
Do Children Perceive Whether a Robotic Peer is Learning or Not
Affect of Robot’s Competencies on Children’s Perception
Synthesizing Robotic Handwriting Motion by Learning from Human Demonstrations
Repositories: